machine learning
correction of chemical property prediction
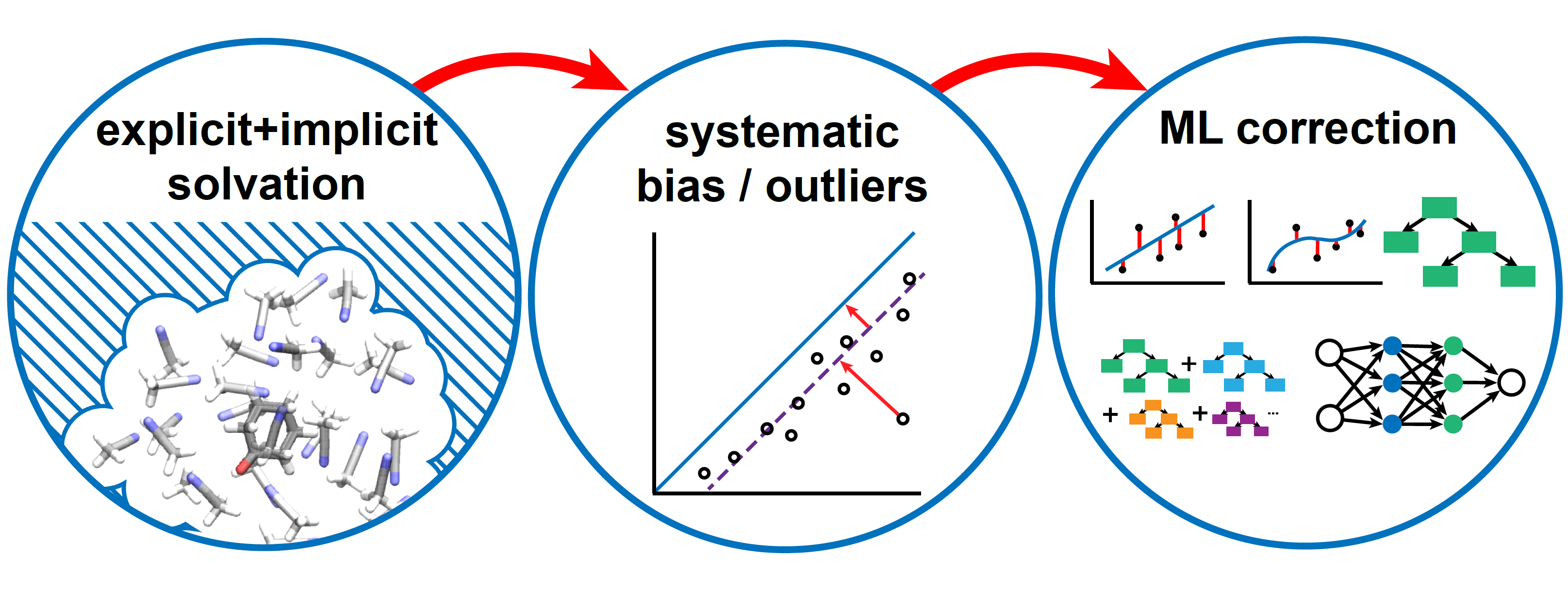
Redox potentials are a fundamental chemical property, where the accuracy of DFT calculations compared to experiments is limited. To improve the accuracy, I ran both high-throughput explicit solvation similation with Autosolvate, and with machine learning reduced the errors between calculations and experimental data, and analysed the error contributions.
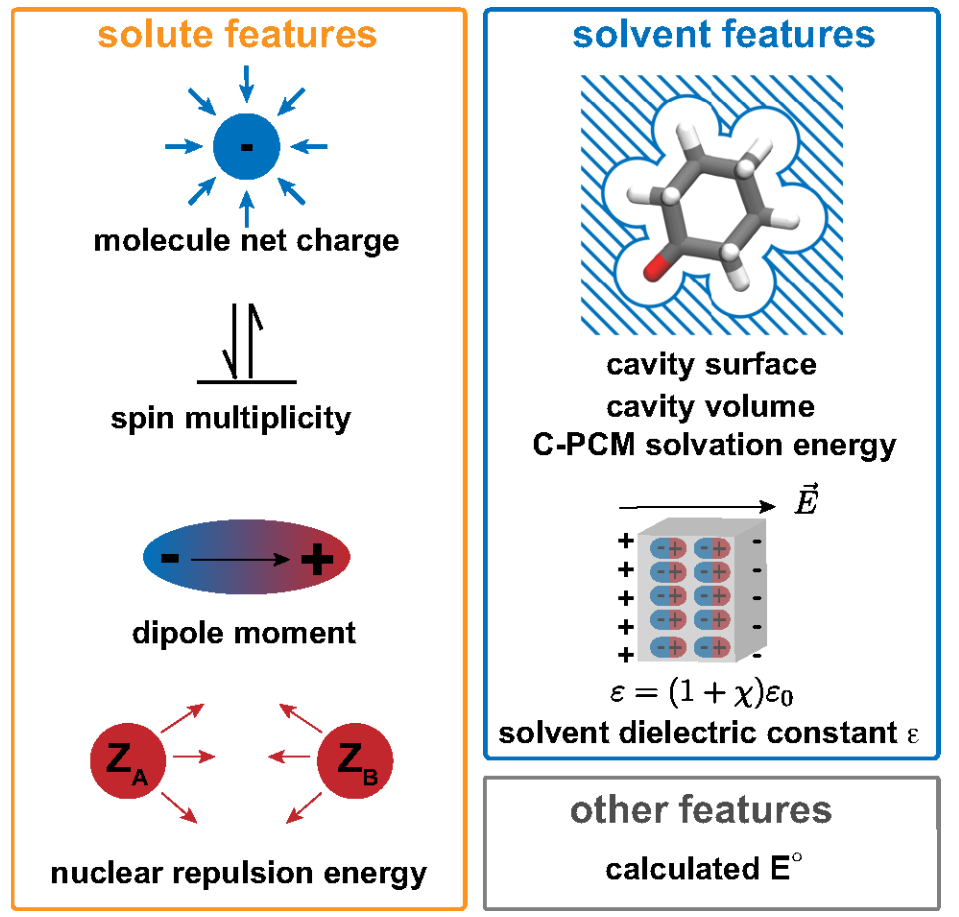
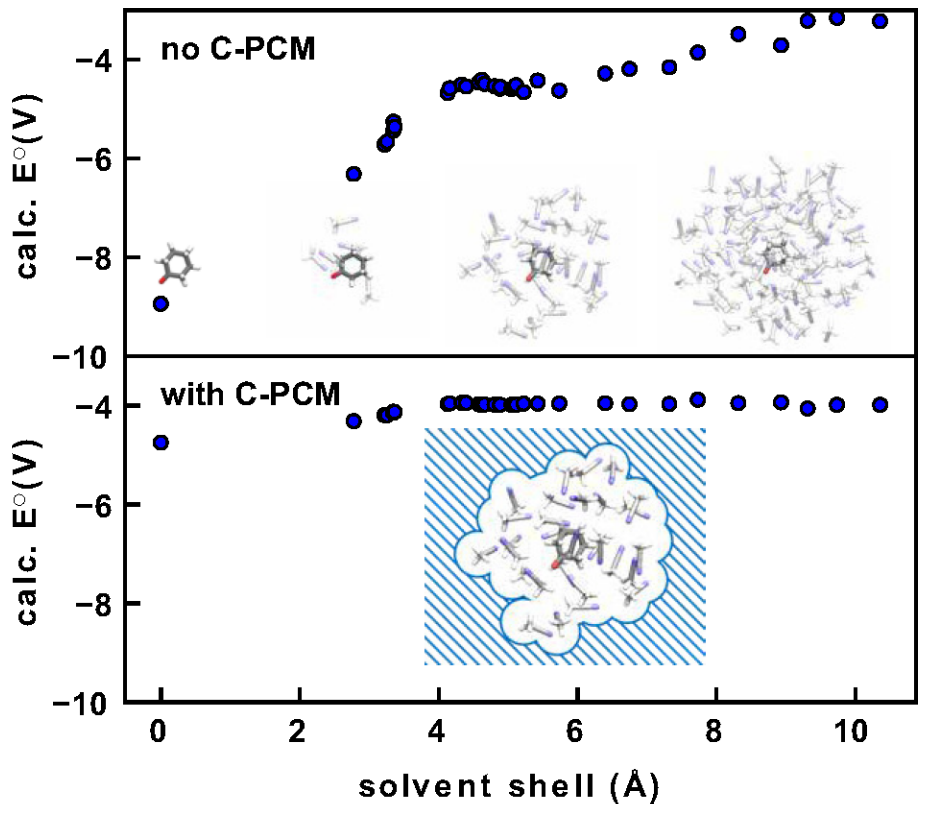
For the low number of redox potential data points, machine learning features related to the solute and solvent were used. To optimize the solvent shell size for redox potential calculation, the convergence of redox potential is shown. When combining an explicit solvent shell with implicit solvent (C-PCM) the convergence is reached much faster at around 4 Å. This reduces the computational requirements to calculate redox potentials with an explicit solvent.
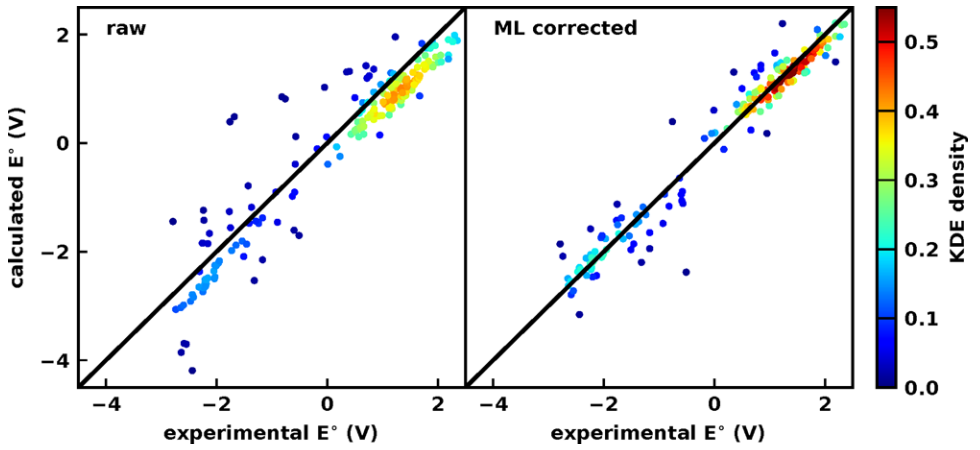
Machine learning could correct both systematic biases and reduce the size of outliers.